This research report compiles 50+ mental health marketing statistics for 2026 for mental health clinics, behavioral health providers, and ABA-focused organizations. It covers the full patient decision cycle, from search behavior and online research to social media exposure, trust and influencer dynamics, online reviews and reputation, and the conversion realities that matter most in healthcare.

WORKS: ▷ Explore Our Mental Health Marketing Done For You Solutions
Mental health marketing in 2026 is shaped by three measurable forces: online research (search-first behavior), social media exposure (mental health content everywhere), and trust signals (reviews, credibility, and response speed). This report compiles the mental health and healthcare marketing statistics you provided into a structured, highly citable resource for mental health clinics, behavioral health practices, and ABA therapy providers.
Table of Contents
Mental Health Demand and Market Growth Statistics
Mental health demand is large, persistent, and structurally underserved. That combination creates a huge “research-first” audience and a fast-growing digital care ecosystem.
Quote-ready summary: In 2024, 23.4% of American adults experienced mental illness, while treatment rates hover around half in the provided data, leaving tens of millions untreated and pushing demand into search, social, and digital care channels.
Mental illness prevalence and treatment gap in the U.S.
The dataset shows mental illness affects more than one in five adults across multiple years, with a large treatment gap.
- 23.4% of American adults (61.5 million) experienced mental illness in 2024.
- 22.8% of U.S. adults experienced mental illness in 2021.
- 5.6% of U.S. adults (14.6 million) had serious mental illness in 2024.
- Only 47.2% of adults with mental illness received treatment in 2021, leaving 42.4 million adults untreated.
- Another estimate in the dataset says 50.6% of U.S. adults with any mental illness receive treatment, reinforcing that roughly half do not.
Market size, digital expansion, and category growth
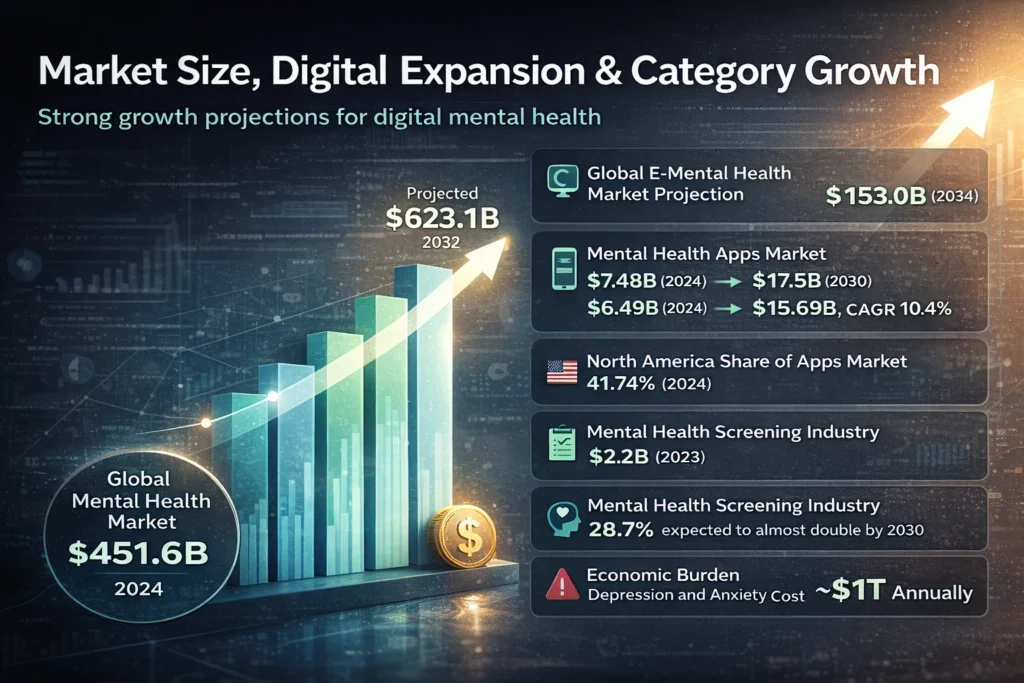
Your dataset shows large market valuations and strong growth projections for digital mental health.
| Category | Stat from dataset |
|---|---|
| Global mental health market | $451.6B (2024) |
| Global mental health market projection | ~$623.1B (2032) |
| Global e-mental health market projection | $153.0B (2034) |
| Mental health apps market (estimate A) | $7.48B (2024) → $17.5B (2030) |
| Mental health apps market (estimate B) | $6.49B (2024) → $15.69B (2033), CAGR 10.4% |
| North America share of apps market | 41.74% (2024) |
| Mental health screening industry | $2.2B (2023), expected to almost double by 2030 |
| Depression/anxiety management share | 28.7% revenue share (2024) |
| Economic burden | Depression and anxiety cost ~$1T annually |
Additional demand indicators in your dataset point to growth in behavioral health medication interest and attention. For example, Adderall prescriptions rose 58.2% among U.S. adults aged 22–44 between 2018 and mid-2022.
Learn More: Best Ads for ABA Therapy Clinics in 2026
Search Behavior and Online Research Statistics
Patients behave like researchers before they behave like patients. Search is not one step, it’s an ongoing loop before contact and after visits.
Quote summary: Healthcare is a major search category (estimated 5–7% of Google searches), and patients rely heavily on search engines before and during care: 65% turn to Google before a doctor, and 77% use search at some point in the care journey.
How much health research happens in Google and search engines
Your dataset includes two estimates of the share of health-related Google searches.
- One estimate says 5% of all Google searches are health-related.
- Another estimate says 7% of all Google searches are health-related.
Even with measurement differences, both support the same conclusion: health is a major search intent category. That demand flows directly into care discovery.
- 77% of patients use search engines at some point in their care journey.
- 75% of people have looked online for information about a specific medical problem.
- 65% of people turn to Google before seeking advice from a doctor.
Based on these numbers, running google ads for mental health clinics is a secure patient acquisition channel in 2026
Online research continues after the visit
Mental health marketing often requires repeated reassurance and consistency. Your dataset shows this behavior is not hypothetical:
- 42% of Americans research their doctors’ recommendations online after a visit.
- 31% say online health research motivates them to prioritize their health and follow up with a doctor.
There’s also an industry-side confirmation that content is not optional anymore: about 70% of healthcare marketing executives have a documented content marketing strategy.
Learn More About The Best Ads for Psychiatrists in 2026
Social Media and Mental Health Awareness Statistics
Social media is now a mental health discovery and awareness layer. People do not just consume content; they learn terminology, compare experiences, and sometimes act on what they see.
Quote-ready summary: Social media is a major health information channel: 55% of adults use it for health info, 58% saw mental health content in the last 30 days, and 23% have sought mental health advice on social platforms.
How prevalent social media use is in the U.S.

The dataset establishes the scale and “time spent” environment where health messaging is competing:
- Roughly 310 million Americans are social media users (2023).
- The average American spends 2 hours 16 minutes per day on social media.
- Platform usage (2024 Pew survey): 85% YouTube, 70% Facebook, 50% Instagram, 36% Pinterest.
- Among teens (13–17), 95% use social media, with about one-third using it “almost constantly.”
Based on these statistics, running facebook ads for mental health clinics is definitely a sound option.
How Americans use social media for health and mental health information
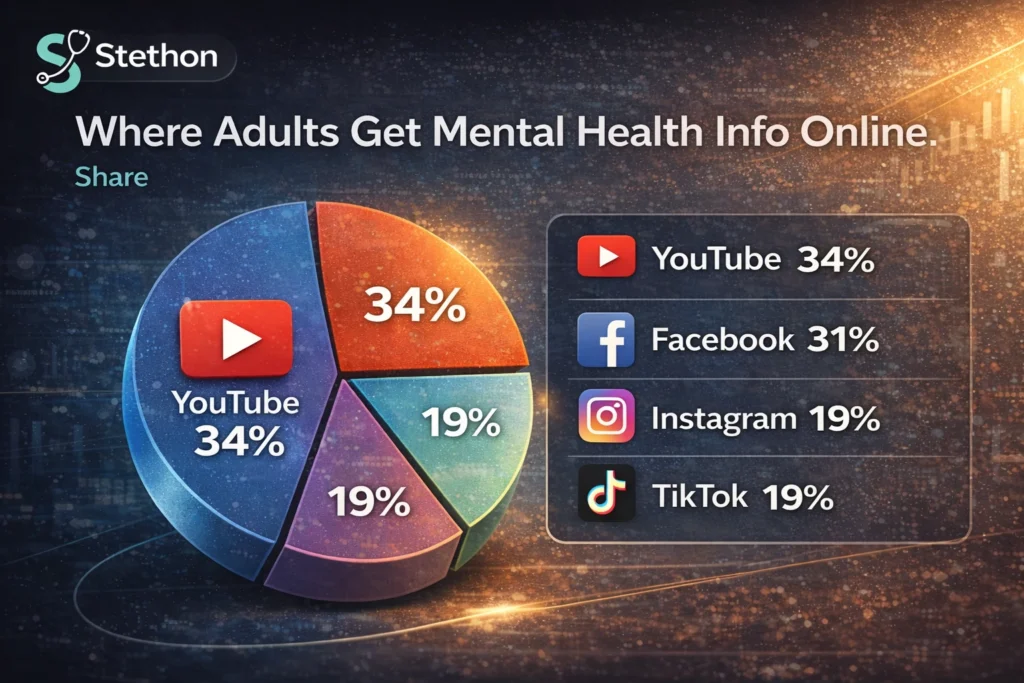
- 55% of U.S. adults use social media to find health information or advice at least occasionally.
- In the past month, 72% saw weight/diet content on social media.
- In the past 30 days, 58% saw mental health content on social media.
- A national survey found 55% of Americans have used social media specifically to look up mental health information, including 77% of young adults 18–34.
When adults seek mental health information online, the dataset indicates where they find it:
| Where adults get mental health info online | Share |
|---|---|
| YouTube | 34% |
| 31% | |
| 19% | |
| TikTok | 19% |
Social can also be a starting point for younger groups:
- 28% of Gen Z and 25% of Millennials begin healthcare research on social platforms.
Read More: Healthcare Advertising Statistics for Clinics in 2026
Mental health awareness behaviors happening on social
Your dataset includes behaviors that matter for clinics because they affect how patients interpret symptoms and whether they self-triage:
- 23% of U.S. adults have actively sought mental health advice on social media.
- In one survey: 55% of Gen Z and 30% of Millennials did so.
- 38% of adults report seeing peers share mental health experiences (up from 30% in 2024).
- 29% learned about mental health disorders via social platforms (up from 22% in 2024).
- In a 2024 poll: 17% discussed social-media-found information with a healthcare professional, and 12% self-diagnosed based on social media content.
Social isn’t only risk. It can also provide support:
- Among people receiving mental health services, 47% say social media makes them feel less alone.
- 67% of adolescents feel more socially supported via social platforms.
Related Article: Reputation Management for Mental Health Clinics in 2026
Trust, Influencers, and Misinformation Statistics
Mental health marketing is credibility marketing. Your dataset shows trust clearly favors credentialed professionals while misinformation exposure is frequent.
Quote-ready summary: Trust strongly favors credentialed professionals: 82% trust mental health info from credentialed providers versus 64% for influencers, while 54% of people report encountering mental health misinformation weekly.
Influencers exist, but trust is limited
- 15% of U.S. adults regularly get health information from social media influencers.
- Among those users, 61% believe influencers are mostly motivated by profit.
- Only 36% of social media health information seekers trust a particular influencer.
Related Article: How to Market a Mental Health Clinic in 2026
Credentialed sources hold a measurable advantage
- 82% of adults trust mental health information from credentialed healthcare professionals.
- 64% trust influencers for health advice.
- 60% of social media users are most likely to trust doctors over any other group.
Misinformation exposure is common
- 54% report encountering mental health misinformation on social media at least weekly.
Online Reviews and Reputation Statistics
Reviews act like a gate to consideration. In local healthcare, they are often the shortlist filter.

Quote-ready summary: Reviews are make-or-break: 94% of patients use online reviews, and 69% won’t consider providers under a 4.0-star rating.
Reviews as a selection filter
- 94% of healthcare patients use online reviews to evaluate providers.
- 84% trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations.
- 74% say reviews are very or extremely important in choosing a provider.
- 69% won’t consider a provider with less than 4.0 stars.
Experience affects retention and switching
- 47% leave medical practices due to poor experiences.
- 43% of Millennials say they are likely to switch providers in the next few years.

Scheduling, Calls, Texting, and Response-Time Statistics
Clinics can spend on mental health local SEO and ads, but conversion often depends on contact systems. The dataset shows phone booking still dominates, while digital expectations and speed expectations keep rising.
Quote-ready summary: Despite rising demand for digital convenience, 88% of appointments are still scheduled by phone, only 2–6% are booked online, and 91% of patients expect a response within 4–24 hours after messaging.
Phone booking still dominates

- 88% of medical appointments are scheduled by phone.
- Only 2–6% are booked online.
- 39% prefer calling for healthcare needs.
- 76% have called a provider during their care journey (as of 2022).
Quick Read: HIPAA training for mental health professionals
Digital scheduling is wanted but underused
- 60% want digital scheduling via portals or apps.
- Mobile scheduling preference jumped 92% from 2018 to 2020.
- Yet only 21% actually booked via computer or mobile app.
Response speed is now part of “patient experience”
- 91% expect a response within 4–24 hours after messaging a provider.
- 49% expect a response within a few hours via social media for appointments or follow-ups.
- 66% prefer text message appointment reminders.
Visuals to create later from this section
- “Digital demand vs reality” split graphic (60% want digital; 88% phone)
- Response expectation clock (4–24 hours; “few hours” on social)
- SMS reminder preference (66%)
Digital Advertising Spend, Costs, and Budget Statistics
Paid acquisition is competitive and expensive. That makes conversion efficiency, trust assets, and operational responsiveness financially important.
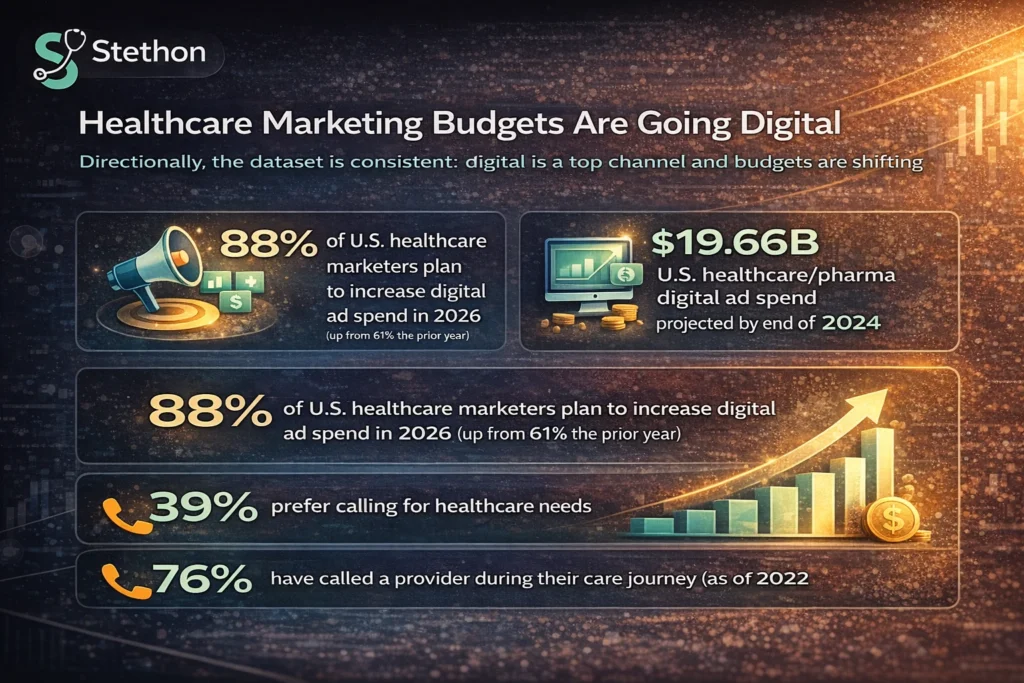
Quote-ready summary: Digital spend is rising in healthcare, with 88% of marketers increasing digital ad spend in 2026, while lead costs average $286 and CPC averages $3.17, pushing clinics to optimize conversion and trust signals.
Digital share and investment direction
Your dataset includes multiple ways reports describe spend mix:
- One stat says 46% of healthcare advertising dollars go to digital (surpassing TV in 2021).
- Another says 40% went to TV in 2021 vs 46% to digital, with the rest in other channels.
- Another references a 46% vs 54% split in 2021 when comparing digital and TV, reflecting classification differences.
Directionally, the dataset is consistent: digital is a top channel and budgets are shifting.
- 88% of U.S. healthcare marketers plan to increase digital ad spend in 2026 (up from 61% the prior year).
- U.S. healthcare/pharma digital ad spend projected at $19.66B by end of 2024.
- U.S. healthcare advertising spending projected to rise from $22.4B (2022) to $29.2B (2028).
Acquisition costs
- Average CPC in health and medical ads is about $3.17.
- Average cost per healthcare lead is roughly $286.
Budget pressure
- Healthcare marketers’ average budget fell to $7.6M (2023) from $8.3M (2022).
- Budgets peaked at $12.5M (2019).
Telehealth, Apps, and Email Marketing Statistics
Digital care adoption and digital engagement are now part of baseline behavioral health marketing strategy.
Quote-ready summary: Telehealth remains far above pre-pandemic levels (38× higher), mental health providers offering digital services rose to 47% from 12%, and healthcare email open rates average 21–22%.
Telehealth and digital services
- Telehealth utilization has stabilized at 38× higher than before the pandemic.
- 47% of mental health providers now offer digital services, up from 12% five years ago.
Mental wellness apps and consumer wellness priority
- Mental wellness app revenue increased 82.5% from 2020–2022, rising from $269M to $491M.
- 84% of U.S. consumers say wellness is a top or important priority.
Email performance
- Average healthcare email open rate is 21–22%.
Practical Worked Example for Mental Health, Behavioral Health, and ABA Clinics
This is a scenario-based blueprint built directly from your dataset. It is not a claim about real results for a specific clinic. It shows how a clinic would align marketing and operations with the behaviors and expectations shown in the statistics.

Quote-ready summary: A 2026-ready behavioral health intake system prioritizes search visibility, clinician-led trust content, review strength, phone-first conversion, and fast response standards, because those are the measurable gates in patient decision-making.
Step 1: Use the dataset to define constraints
A clinic must operate inside these facts:
- People research before contacting: 65% go to Google before seeking advice and 77% use search in the journey.
- Social exposure is high: 58% saw mental health content recently and 23% sought mental health advice on social.
- Trust favors credentialed voices: 82% trust credentialed professionals versus 64% influencers, while 54% see misinformation weekly.
- Reviews are a conversion gate: 94% use reviews and 69% reject providers under 4.0 stars.
- Phone still closes bookings: 88% of appointments are scheduled by phone.
- Speed is expected: 91% expect responses within 4–24 hours after messaging.
Step 2: Build the system around those constraints
A clinic aligned with the dataset would design around:
- Search-first discovery content because patients start on Google and continue researching after visits.
- Clinician-led social education because credibility and trust favor professionals and misinformation is frequent.
- A review engine because reviews are a shortlist filter and ratings thresholds are explicit in the data.
- Phone-first intake conversion because bookings still happen by phone at scale.
- Fast response standards because response time is now part of patient experience expectations.
Building ppc campaigns for mental health clinics is usually the first patient acquisition system to be built in 2026.
Step 3: Track the KPIs implied by the statistics
- Time-to-first-response on messages (aligned with 4–24 hour expectation).
- Social inquiry response speed (aligned with “few hours” expectation).
- Phone answer rate and booked appointment rate (aligned with 88% phone scheduling reality).
- Review velocity and average rating (aligned with the 4.0-star threshold).
- Lead-to-appointment conversion efficiency (aligned with $286 lead cost pressure).
Key Takeaways

Mental health marketing statistics in your dataset repeatedly point to the same conclusion: growth is constrained or unlocked by trust and conversion systems, not just by traffic.
- Healthcare is a major search category and patients rely on search heavily before and during care.
- Social media is now a mental health awareness layer, particularly for younger cohorts.
- Credentialed trust wins, while misinformation exposure is frequent.
- Reviews act like a hard gate to consideration, including a clear 4.0-star threshold.
- Phone scheduling still dominates, while speed and digital convenience expectations keep rising.
- Paid acquisition is expensive, which increases the value of conversion efficiency.
Sources and Editorial Disclaimer
This is a research-driven, data-first report produced by Stethon Digital Marketing. It is built to be highly practical for mental health clinics, behavioral health providers, and ABA-focused organizations.
Industry statistics used: The statistics in this report come from the dataset supplied for this article. Within that dataset, the figures are described as drawn from authoritative surveys and reports, including references to Pew Research, HHS / U.S. Surgeon General advisory, APA polling, KFF surveys, and SAMHSA / NIMH-referenced data, alongside healthcare and marketing industry research studies.
How this report was created: We organized the dataset into the stages that matter in real patient acquisition and retention (search discovery, social exposure, trust and reviews, contact behavior, and response expectations). Where the dataset includes multiple estimates for similar metrics, we present them transparently as provided rather than forcing a single number.
Stethon practitioner context: The interpretation and recommendations reflect Stethon’s hands-on healthcare marketing experience and pattern recognition from real campaigns, including insights informed by aggregated performance learnings across client work (e.g., intake conversion constraints, reputation thresholds, response-time expectations, and channel mix realities). No individually identifiable client information is included.
Disclaimer: This content is for marketing and research purposes only and does not provide medical advice. It is an editorial synthesis of the supplied data, not a peer-reviewed academic publication. Results and benchmarks vary by specialty, geography, payer mix, and operational capacity.
